HashiCorp Vault and GCP workloads: a draft process for secure credential retrieval
Brief introduction
Hello world!
This is my first article and I’ll briefly discuss a solution for securely retrieving secrets stored in a self-hosted HashiCorp Vault server from Google Cloud Platform workloads, such as Cloud Run apps or PySpark jobs running on Dataproc clusters.
This approach avoids the need to set pre-shared authentication tokens inside of any environment variables and it originated from professional activities in order to make it reusable and standardizable (at your company or for personal purposes).
The presented solution requires an initial setup to enable the integration between HashiCorp Vault and GCP, along with a simple code template for credential retrieval: this code snippet should be executed before running any business logic that requires access to secrets.
Let’s dive in!
Initial Setup
First of all, check that HashiCorp Vault server is accessible from your chosen GCP execution environment and enable IAM Service Account Credentials API on your GCP project.\
Refer to the official documentation about IAM Service Account Credentials API: Google Cloud IAM Service Account Credentials API Documentation
Next, you need to create a dedicated service account with Service Account Token Creator IAM role that impersonates itself.
Further details at the following page: Create Short-Lived Credentials with Service Account Token Creator
The final step involves enabling the GCP authentication method on your HashiCorp Vault server, please follow the official documentation for configuring this: Configure the GCP Authentication Method in HashiCorp Vault
Overview
Here is a general flowchart for illustrating how it works.
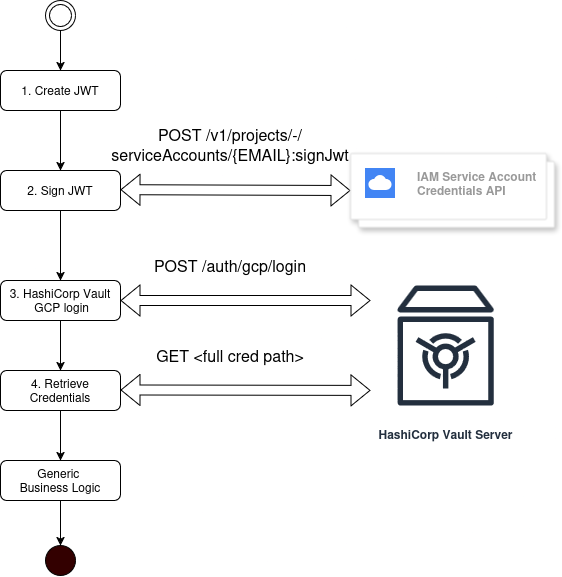
Step 1
The JWT authentication token is created with the following claims:
- sub -> Use service account email address as subscriber
- aud -> Use the name of your defined role in HashiCorp Vault server
- iat -> Issued At Time
- exp -> Expiry Time
Further details at: Generating Jwts
Step 2
Next, signJwt operation is done by calling its IAM Service Account Credentials endpoint, in order to sign the previously generated JWT.
Documentation: IAM Service Account Credentials signJwt
“projects/-/serviceAccounts/
Step 3
Once you get the signed JWT, GCP authentication could be done by calling Vault GCP login API and in case of success a special token named client_token is returned.
Details: Vault GCP Login
Step 4
As last step, credentials could be successfully retrieved and used by passing the client token in the custom HTTP header X-Vault-Token.
Code template (python)
import http.client
import ssl
import json
import datetime
from google.cloud import iam_credentials_v1
def get_credentials():
now = datetime.datetime.now()
exp = now + datetime.timedelta(minutes=<minutes>)
# 1. Create JWT
jwt = {
"sub": "<your service account email address>",
"aud": "vault/<your defined HashiCorp Vault role>",
"exp": int(exp.timestamp()),
"iat": int(now.timestamp()),
}
# 2. Sign JWT
sign_jwt_request = iam_credentials_v1.SignJwtRequest(
name="projects/-/serviceAccounts/<your service account email address>",
payload=json.dumps(jwt),
)
sign_jwt_response = client.sign_jwt(request=sign_jwt_request)
# 3. HashiCorp Vault GCP Auth
vault_conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection("<your HashiVorp Vault server URL>")
vault_auth_json_body = {"role": "<your defined HashiCorp Vault role>", "jwt": sign_jwt_response.signed_jwt}
vault_conn.request("POST", "<base path>/auth/gcp/login", json.dumps(vault_auth_json_body))
vault_response = vault_conn.getresponse()
vault_response_data = json.loads(vault_response.read().decode("utf-8"))
# 4. Get credentials
headers = {"X-Vault-Token": vault_response_data["auth"]["client_token"]}
vault_conn.request(
"GET",
"<base path>/<credential path>",
headers=headers,
)
credentials_response = vault_conn.getresponse()
I believe a potential improvement could involve leveraging the HashiCorp Vault community library hvac, exploring alternative HTTP client libraries and adding error handling logic.
Conclusions
I hope it could be useful for developers and cloud engineers looking to enhance the security of their applications running on GCP, ensuring that secrets are accessed securely and efficiently and reducing the risk of exposure and misuse.
I have nothing else to add at the moment and I’ll consider writing a follow-up article with further details and applied improvements.
I wish you all the best,
f4berack